二叉树属性
一个有效的树中,如果有N个节点就会有N-1条边。
深度:树的节点X的深度被定义为从根到节点X的路径长度。路径上的每一条边贡献一个长度单位。根的深度是0。
高度:树的节点X的高度被定义为从该节点到一个叶子节点的最长路径上的边数。叶子节点的高度是0。
树的高度:树的高度等于根节点的高度。
二叉树:一个树中的每个节点最多含有两个子节点(children) ,这个树被称为二叉树。
树的实现方式:动态创建节点,用指针或者引用把他们链接起来。
二叉树:每个节点有三个域,其中一个用来存放数据,其它两个为指向节点的指针。一个存储左孩的地址,另一个存储右孩的地址。
# 二叉树属性题
# 1.1.对称二叉树 (opens new window)
给你一个二叉树的根节点
root, 检查它是否轴对称。示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 输出:true1
2示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 输出:false1
2
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
if (not root.left) ^( not root.right):
return False
queue = collections.deque([root.left, root.right])
while queue:
cur1 = queue.popleft()
cur2 = queue.popleft()
if (not cur1) ^ (not cur2):
return False
if cur1 and cur2:
if cur1.val != cur2.val:
return False
queue.append(cur1.left)
queue.append(cur2.right)
queue.append(cur1.right)
queue.append(cur2.left)
return True
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.2二叉树的最大深度 (opens new window)
给定一个二叉树
root,返回其最大深度。二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
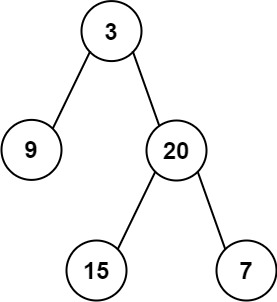
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:31
2示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2] 输出:21
2
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
"""
广度优先遍历,最大深度就是遍历的层数
"""
if not root:
return 0
queue = collections.deque([root])
ret = 0
while queue:
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
ret += 1
return ret
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
"""
深度优先遍历
"""
def height(root):
if not root:
return 0
return max(height(root.left), height(root.right))+1
return height(root)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# [1.3.二叉树的最小深度](111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode) (opens new window))
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
**说明:**叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:21
2示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6] 输出:51
2提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 105]内-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
left = root.left
right = root.right
min_depth = float("inf")
if not left and not right:
return 1
if left:
min_depth = min(self.minDepth(left), min_depth)
if right:
min_depth = min(self.minDepth(right), min_depth)
return min_depth + 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
var height func(root *TreeNode) int
height = func(root *TreeNode) int{
if root == nil{
return 0
}
if (root.Left == nil) && (root.Right == nil){
return 1
}
minD := math.MaxInt32
if root.Left != nil{
minD = min(height(root.Left), minD)
}
if root.Right != nil{
minD = min(height(root.Right), minD)
}
return minD + 1
}
return height(root)
}
func min(a, b int ) int{
if a>b{
return b
} else{
return a
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.4. 完全二叉树的节点个数 (opens new window)
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点
root,求出该树的节点个数。完全二叉树 (opens new window) 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第
h层,则该层包含1~ 2h个节点。示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6] 输出:61
2示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:01
2示例 3:
输入:root = [1] 输出:11
2
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
"""
深度优先遍历
"""
def height(root):
if not root:
return 0
#return max(height(root.left), height(root.right))+1
# 上面的写法等价于
leftdepth = height(root.left) +1
rightdepth = height(root.right) + 1
return max(leftdepth, rightdepth)
return height(root)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.5. 平衡二叉树 (opens new window)
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是
平衡二叉树
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:true1
2示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4] 输出:false1
2示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:true1
2
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
# 左右子树高度不超过1
def depth(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
leftdepth = depth(root.left) + 1
rightdepth = depth(root.right) + 1
return max(leftdepth, rightdepth)
# 如果这个树是二叉树,左右子树高度差< 1, 并且左右子树均为二叉树
if not root:
return True
return True if (abs(depth(root.left)- depth(root.right))<=1 and self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right)) else False
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.6二叉树的所有路径 (opens new window)
给你一个二叉树的根节点
root,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,5] 输出:["1->2->5","1->3"]1
2示例 2:
输入:root = [1] 输出:["1"]1
2
笔记
递归+回溯
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def binaryTreePaths(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[str]:
ret = list()
def dfs(root, path):
if not root:
return
path.append(str(root.val))
if root.left==None and root.right == None:
ret.append( "->".join(path[:]))
return
if root.left:
dfs(root.left, path)
path.pop()
if root.right:
dfs(root.right, path)
path.pop()
dfs(root,[])
return ret
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func binaryTreePaths(root *TreeNode) []string {
ret := make([]string, 0)
path := make([]string, 0)
var dfs func(root *TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode){
if root == nil{
return
}
path = append(path, strconv.Itoa(root.Val))
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil{
temp := make([]string, len(path))
copy(temp, path)
ret = append(ret, strings.Join(temp, "->"))
return
}
if root.Left != nil{
dfs(root.Left)
path = path[:len(path)-1]
}
if root.Right != nil{
dfs(root.Right)
path = path[:len(path)-1]
}
}
dfs(root)
return ret
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.7.左叶子之和 (opens new window)
给定二叉树的根节点
root,返回所有左叶子之和。示例 1:
输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出: 24 解释: 在这个二叉树中,有两个左叶子,分别是 9 和 15,所以返回 241
2
3示例 2:
输入: root = [1] 输出: 01
2
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root, isLeft):
if not root:
return 0
ret = 0
if (not root.left) and (not root.right) and (isLeft):
ret = ret + root.val
return ret
if root.left:
ret +=dfs(root.left, True)
if root.right:
ret += dfs(root.right, False)
return ret
ret = dfs(root, False)
return ret
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
class Solution:
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
ret = 0
def dfs(root):
if not root:
return 0
ret = 0
if (root.left) and (not root.left.left) and (not root.left.right):
ret = ret + root.left.val
ret += dfs(root.left)
ret += dfs(root.right)
return ret
ret = dfs(root)
return ret
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := 0
var dfs func(node *TreeNode, isLeft bool)
dfs = func(node *TreeNode, isLeft bool){
if node == nil{
return
}
if isLeft== true && node.Left == nil && node.Right ==nil{
ans += node.Val
}
dfs(node.Left, true)
dfs(node.Right, false)
return
}
dfs(root, false)
return ans
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := 0
var dfs func(node *TreeNode)
dfs = func(node *TreeNode){
if node == nil{
return
}
if node.Left != nil && node.Left.Left == nil && node.Left.Right ==nil{
ans += node.Left.Val
}
dfs(node.Left)
dfs(node.Right)
return
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.8找树左下角的值 (opens new window)
给定一个二叉树的 根节点
root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
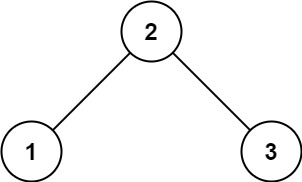
输入: root = [2,1,3] 输出: 11
2示例 2:
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7] 输出: 71
2
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def findBottomLeftValue(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
queue = collections.deque([root])
while queue:
temp = collections.deque()
for i in range(len(queue)):
cur = queue[i]
if cur.left:
temp.append(cur.left)
if cur.right:
temp.append(cur.right)
if len(temp)==0:
break
queue = temp
return queue[0].val
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func findBottomLeftValue(root *TreeNode) int {
// 层序遍历取最后一层的第一个
queue := []*TreeNode{}
queue = append(queue, root)
for len(queue)>0{
temp := []*TreeNode{}
n := len(queue)
for i:=0;i<n;i++{
cur := queue[i]
if cur.Left != nil{
temp = append(temp, cur.Left)
}
if cur.Right != nil{
temp = append(temp, cur.Right)
}
}
if len(temp) == 0{
break
}
queue = temp
}
return queue[0].Val
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.9.路径总和 (opens new window)
给你二叉树的根节点
root和一个表示目标和的整数targetSum。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和targetSum。如果存在,返回true;否则,返回false。叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true 解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。1
2
3示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:false 解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径: (1 --> 2): 和为 3 (1 --> 3): 和为 4 不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。1
2
3
4
5
6示例 3:
输入:root = [], targetSum = 0 输出:false 解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。1
2
3
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.10路径总和 (opens new window)
给你二叉树的根节点
root和一个表示目标和的整数targetSum。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和targetSum。如果存在,返回true;否则,返回false。叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22 输出:true 解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。1
2
3示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:false 解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径: (1 --> 2): 和为 3 (1 --> 3): 和为 4 不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。1
2
3
4
5
6示例 3:
输入:root = [], targetSum = 0 输出:false 解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。1
2
3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
def dfs(root, num):
if root == None:
return False
if root.left == None and root.right == None and num == targetSum:
return True
if root.left:
tag = dfs(root.left, num + root.left.val)
if tag:
return True
if root.right:
tag = dfs(root.right, num + root.right.val)
if tag:
return True
return False
return dfs(root, root.val)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
queue1 = collections.deque([root])
queue2 = collections.deque([root.val])
while queue1:
cur = queue1.popleft()
num = queue2.popleft()
if cur.left == None and cur.right==None and num == targetSum:
return True
if cur.left:
queue1.append(cur.left)
queue2.append(num + cur.left.val)
if cur.right:
queue1.append(cur.right)
queue2.append(num+cur.right.val)
return False
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
// 深度优先算法
if root == nil{
return false
}
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, num int) bool
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, num int) bool {
if root == nil{
return false
}
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil && num == targetSum{
return true
}
if root.Left != nil{
tag := dfs(root.Left, num + root.Left.Val)
if tag == true{
return true
}
}
if root.Right != nil{
tag := dfs(root.Right, num + root.Right.Val)
if tag == true{
return true
}
}
return false
}
return dfs(root, root.Val)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
// 广度优先算法
if root == nil{
return false
}
queue1 := []*TreeNode{root}
queue2 := []int{root.Val}
for len(queue1)>0{
cur := queue1[0]
num := queue2[0]
queue1 = queue1[1:]
queue2 = queue2[1:]
if num == targetSum && cur.Left == nil && cur.Right == nil{
return true
}
if cur.Left != nil{
queue1 = append(queue1, cur.Left)
queue2 = append(queue2, num + cur.Left.Val)
}
if cur.Right != nil{
queue1 = append(queue1, cur.Right)
queue2 = append(queue2, num + cur.Right.Val)
}
}
return false
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group