二叉搜索树修改与构造
二叉搜索树修改与构造
# 二叉搜索树修改与构造
二叉搜索树中的插入操作
# 1.1. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作 (opens new window)
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点
root和要插入树中的值value,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果 。
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5 输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5] 解释:另一个满足题目要求可以通过的树是:1
2
3示例 2:
输入:root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25 输出:[40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]1
2示例 3:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5 输出:[4,2,7,1,3,5]1
2
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def insertIntoBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
node = TreeNode(val=val)
if not root:
return node
curNode = root
parentNode = TreeNode(val= val)
while curNode:
if val < curNode.val:
parentNode = curNode
curNode = curNode.left
else:
parentNode = curNode
curNode = curNode.right
if val < parentNode.val:
parentNode.left = node
else:
parentNode.right = node
return root
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func insertIntoBST(root *TreeNode, val int) *TreeNode {
// 二叉搜索树中序遍历的结果是顺序的,判断新插入的值是不是在两个pre.val < val < next.val
// 此时pre.val, 和next.val就是要插入的数值
insertNode := &TreeNode{Val: val}
if root == nil{
return insertNode
}
parentNode := &TreeNode{}
currentNode := root
for currentNode != nil{
if val<currentNode.Val{
parentNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.Left
} else{
parentNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.Right
}
}
if val <parentNode.Val{
parentNode.Left = insertNode
}else{
parentNode.Right = insertNode
}
return root
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.2. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点 (opens new window)
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
- 首先找到需要删除的节点;
- 如果找到了,删除它。
示例 1:
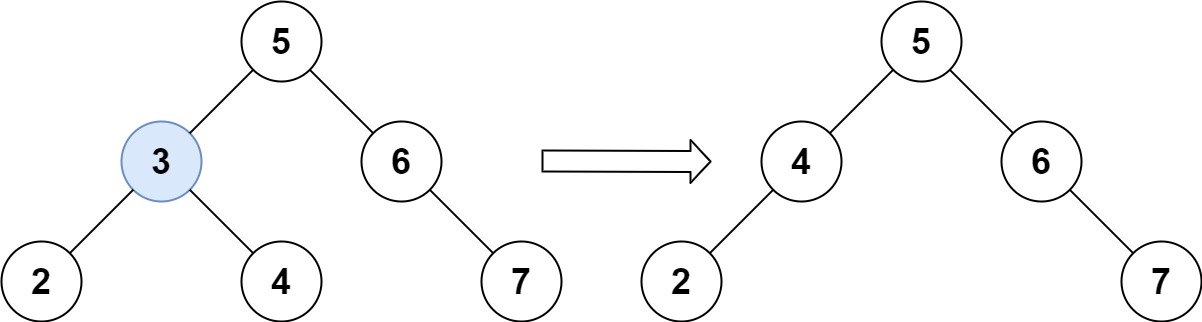
输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3 输出:[5,4,6,2,null,null,7] 解释:给定需要删除的节点值是 3,所以我们首先找到 3 这个节点,然后删除它。 一个正确的答案是 [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], 如下图所示。 另一个正确答案是 [5,2,6,null,4,null,7]。1
2
3
4
5示例 2:
输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0 输出: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7] 解释: 二叉树不包含值为 0 的节点1
2
3示例 3:
输入: root = [], key = 0 输出: []1
2
笔记
二叉搜索树有以下性质:
左子树的所有节点(如果有)的值均小于当前节点的值; 右子树的所有节点(如果有)的值均大于当前节点的值; 左子树和右子树均为二叉搜索树
根据二叉搜索树的性质
如果目标节点大于当前节点值,则去右子树中删除;
如果目标节点小于当前节点值,则去左子树中删除;
如果目标节点就是当前节点,分为以下三种情况:
其无左子:其右子顶替其位置,删除了该节点;
其无右子:其左子顶替其位置,删除了该节点;
其左右子节点都有:其左子树转移到其右子树的最左节点的左子树上,然后右子树顶替其位置,由此删除了该节点。
后续补充
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group
# 1.3. 修剪二叉搜索树 (opens new window)
给你二叉搜索树的根节点
root,同时给定最小边界low和最大边界high。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[low, high]中。修剪树 不应该 改变保留在树中的元素的相对结构 (即,如果没有被移除,原有的父代子代关系都应当保留)。 可以证明,存在 唯一的答案 。所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。注意,根节点可能会根据给定的边界发生改变。
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2 输出:[1,null,2]1
2示例 2:
输入:root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3 输出:[3,2,null,1]1
2
笔记
如果一个结点 node符合要求,即它的值位于区间 [low,high],那么它的左子树与右子树应该如何修剪?
我们先讨论左子树的修剪:
node 的左结点为空结点:不需要修剪
node 的左结点非空:
如果它的左结点 left 的值小于 low,那么 left 以及 left 的左子树都不符合要求,我们将 node的左结点设为 left的右结点,然后再重新对 node\的左子树进行修剪。
如果它的左结点 left 的值大于等于 low,又因为 node 的值已经符合要求,所以 left 的右子树一定符合要求。基于此,我们只需要对 left的左子树进行修剪。我们令 node 等于 left,然后再重新对 node 的左子树进行修剪。
以上过程可以迭代处理。对于右子树的修剪同理。
我们对根结点进行判断,如果根结点不符合要求,我们将根结点设为对应的左结点或右结点,直到根结点符合要求,然后将根结点作为符合要求的结点,依次修剪它的左子树与右子树。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def trimBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
while root and (root.val <low or root.val > high):
if root.val < low:
root = root.right
else:
root = root.left
node = root
while node.left:
if node.left.val < low:
node.left = node.left.right
else:
node = node.left
node = root
while node.right:
if node.right.val > high:
node.right = node.right.left
else:
node = node.right
return root
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
笔记
对根节点进行深度优先遍历,对于当前访问的节点,如果节点为空,直接返回空节点
如果节点的值小于low,那么说明该节点以及他的左节点都不符合要求,此时我们返回对他的右节点的修剪结果
如果节点的值大于high,那么说明该节点以及他的右节点都不符合要求, 此时我们返回对的他的左节点的修剪结果
如果结点的值位于区间 [low,high][\textit{low}, \textit{high}][low,high],我们将结点的左结点设为对它的左子树修剪后的结果,右结点设为对它的右子树进行修剪后的结果
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def trimBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None:
return None
if root.val < low:
return self.trimBST(root.right, low, high)
if root.val > high:
return self.trimBST(root.left, low, high)
root.left = self.trimBST(root.left, low, high)
root.right = self.trimBST(root.right, low, high)
return root
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func trimBST(root *TreeNode, low int, high int) *TreeNode {
for root != nil && (root.Val < low || root.Val > high){
if root.Val < low{
root = root.Right
} else{
root = root.Left
}
}
if root == nil{
return nil
}
node := root
for node.Left != nil{
if node.Left.Val < low{
node.Left = node.Left.Right
} else{
node = node.Left
}
}
node = root
for node.Right != nil{
if node.Right.Val >high{
node.Right = node.Right.Left
} else{
node = node.Right
}
}
return root
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
// Make sure to add code blocks to your code group